Macintosh II Family Technical Overview
[Amiga] [Apollo] [Atari] [Mac II] [Mac Entry Level] [Mac Quadra] [Mac AV] [NeXT Architecture] [Radius Rocket] [Sun 3 Series]
Overview
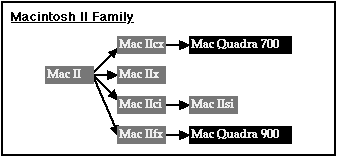
This page documents the Macintosh II family which includes the II, IIx, IIfx, IIcx, IIci, IIsi, and IIvx as well as others. The Macintosh II family is based around the Motorola 68030 processor with exception of the Macintosh II which had a Motorola 68020 processor.
Figure 1.1 Macintosh Evolustion
The Macintosh II was eXtened with the Macintosh IIx and the Compact Macintosh IIcx. A super-god like special eFfects whiz-bang totally bitchin' computer was created called the Macintosh IIfx. Later models with Integrated video were created called the Macintosh IIci and the Macintosh IIsi.
Later the Quadra 700 computer was introduced and its design was derived from the Macintosh IIcx computer. The Macintosh IIfx lived on as well in the Quadra 900 and later the Quadra 950 as well. The Quadra 700 evolved into future versions of more power Quadra computers and the first PowerMacintosh line as well. The Macintosh IIfx legacy and IOP controllers never lived on beyond the Quadra 950 or similar WorkGroup servers. The IIci with its cheap RAM Based Video evolved to the inferior Macintosh IIsi, a slower IIci without cache, nor expansion. The IIsi only had a PDS slot which can be used with an adaptor as one NuBus slot. This is a hard decision for those deciding between acceleration, ethernet, or more well thought out video system.
Figure 1.2 Macintosh LifeSpans (as per AppleFacts)
Linux/m68k (macLinux) Notes
Generally Linux/m68k runs on any 68020 with an PMMU processor. It is good to have an math (fpu) processor as it is slow to use an emulator. The 68030 have a buit-in MMU (memory management unit) and the 68040 have a built-in math coprocessor (fpu) as well.
Linux/m68k currently runs on a variety of Macintosh II computers. The Macintosh II computer needs a PMMU processor installed into the available socket, while the other computers have a built-in MMU module within the 68030 processor. An MMU unit is needed to address memory of 32bits and to translate between 32bit and 24 bit addressing.
Currently the Macintosh IIfx does not have the needed support to get this machine to work properly. There are two IOP6502 ICs which control the floppy/serial and adb. Without public documentation, keyboard, mouse, floppy, and serial may not function.
Components
The following is a list of the components that make up the capabilities of the Macintosh II Family line:
- SWIM (Steve Woz Integrated Machine) controls the floppy drives and supports 1.44 MB floppies. This replaces the older IWM (Integrated Woz Machine) which only offers support 800K floppies.
- SCC (Serial Communications Controller) is an 8530 and provides independent ports for serial communication.
- ADB (Apple Desktop Bus) is a bus for supporting up to 7 different devices daisy chained onto each other. There are 16 addresses, and multiple-devices like a trackball and a mouse can connected and utilized.
- SCSI (Small System Interface) is built-in all Macintosh computers. The Macintosh II family uses the 5380 chipset which supports 8bit transfers, with exception of the Macintosh IIfx which has a modefied version that supports 32bit transfers and DMA access.
- ASC (Apple Sound Chip) supports 8 bit stereo audio output which made Macintosh famous for their sound capabilities until the arrival of SoundBlaster in the open PC Clone market.
- RBV (RGB Built-In Video) - This mechanism uses the BrookTree chipset to drive video using the processor's memory. This interface, while lower the cost per unit, saves Apple money at the customer's expense because the performance could downgrade RAM access by more than 40%. The Macintosh IIci and Macintosh IIsi use the RBV chipset.
- IOP (Input/Output Processor) - This is a 6502 processor that can control other devices. There are two in the Macintosh IIfx where one IOP controls the ADB and SWIM while the other controls SCC.
Ports
All Macintosh II series of computers contained the following ports located in the back of the computer:
sound 1/8" jack (8 bit stereo) out
two ADB ports for mouse and keyboards
two serial/printer ports (RS422 8 mini-din)
SCSI-1 (DB25) The Macintosh IIcx, Macintosh IIci and Macintosh IIsi also contained the following ports:
SuperDrive Floppy port (DB19) The Macintosh IIci , IIsi, IIvi and IIvx also contained edthe following ports:
1 RGB Video port (DB15) The Macintosh IIsi, Macintosh IIvi, and Macintosh IIvx had recording circuitry and thus also contained the following ports:
1 sound 1/8" jack (8 bit mono) microphone input
StatisticsMacintosh II (3/87 to 1/90)
- Processor: 16Mhz MC68020 CPU and MC68881 FPU (socket for MC68851 MMU)
- Bus Speed: 16Mhz
- Memory ICs: GLUE
- Control ICs: 2 VIAs
- Floppy: IWM (Integrated Woz Module) for 800K floppies
- Ports:

- Expansion: 6 Nubus Slots (0x09 to 0x0E)
Macintosh SE/30 (1/89 to 11/91)
- Processor: 16Mhz MC68020 CPU and MC68881 FPU (socket for MC68851 MMU)
- Bus Speed: 16Mhz, 32bits
- Memory ICs:
- Control ICs: 2 VIAs
- Floppy: SWIM for FDHD SuperDrive (1.44meg floppies)
- Ports:

- Expansion: 030 PDS (120 pin 030 )
Macintosh IIcx
and IIx
- Processor: 16Mhz MC68030 and MC68882
- Bus Speed: 16Mhz, 32bit
- Memory ICs: GLUE
- Control ICs: 2 VIAs
- Floppy: SWIM for FDHD SuperDrive (1.44meg floppies)
- Ports:
- IIcx:

- IIx:

- Expansion: 3 Nubus Slots (0x09 to 0x0B) or 6 Nubus Slots
Macintosh IIfx (3/90 to 10/91)
- Processor: 40Mhz MC68030 and MC68882
- Bus Speed: 40Mhz and 20Mhz, 32bit*
- Memory ICs: OSS and FMC (Fast Memory Controller)
- Control ICs: 1 VIA and OSS (Operating System Services)
- Floppy: SWIM for FDHD SuperDrive (1.44meg floppies)
- Ports:

- Expansion: 6 Nubus Slots and IIfx PDS (Processor Direct Slot)
*The direct cache and memory operated at 40Mhz, while the rest of the bus operated at 20Mhz. There was a IC that managed the ossilation between 20Mhz and 40Mhz.
Macintosh IIci (9/89 to 1/93)
- Processor: 25Mhz MC68030 and MC68882
- Bus Speed: 25Mhz, 32bit
- Memory ICs: MDU (Memory Decode Unit) and RBV
- Control ICs: 1 VIA and RBV (RAM Based Video)
- Floppy: SWIM for FDHD SuperDrive (1.44meg floppies)
- Ports:
- Expansion: 3 Nubus Slots (0x0C to 0x0E)
Macintosh IIsi (10/90 to 2/93)
- Processor: 20Mhz MC68030 and MC68882
- Bus Speed: 20Mhz, 32bit
- Memory ICs: MDU (Memory Decode Unit) and RBV
- Control ICs: 1 VIA and RBV (RAM Based Video)
- Floppy: SWIM for FDHD SuperDrive (1.44meg floppies)
- Expansion: 030 PDS (120 pin 030*)
*This is identical to the Macintosh SE/30 PDS slot. It is different that the PDS slot introduced in the Macintosh LC.
Macintosh IIvi (10/92 to 10/93)
- Processor: 16Mhz MC68030 and MC68882
- Bus Speed:
- Memory ICs:
- Control ICs:
- Floppy: SWIM for FDHD SuperDrive (1.44meg floppies)
- Expansion: 3 Nubus slots
Macintosh IIvi (10/92 to 10/93)
- Processor: 32Mhz MC68030 and MC68882
- Bus Speed:
- Memory ICs:
- Control ICs:
- Floppy: SWIM for FDHD SuperDrive (1.44meg floppies)
- Expansion: 3 Nubus slots
FeaturesMacintosh IIci
- Integrated RAM Based Video - This was the first MacII to included built-in video. Usage of this can slow RAM access by over 40%. To improve performance, NuBus video card is usually installed.
- Cache slot - SRAM Cache SIMM can be added to improve performance.
Macintosh IIfx
- IOP proccessor - Used to offload I/O processing from the main processor to these 6502 processors.
- SCSI DMA - Powerful SCSI with DMA access which dramatically improves performance.
- 32KB cache - Built-in high speed cache assures a no-wait state. This dramatically improves performance by up to 30% as the processor no longer wastes processing cycles waiting for memory.
Macintosh IIsi
- Audio Input (8bit mono)
- Integrated RAM Based Video - This was the first MacII to include built-in video. Usage of this can slow RAM access by over 40%. To improve performance, NuBus video card is usually installed.
Macintosh IIvx and Macintosh IIvi
- Audio Input (8bit mono)
- Integrated Video Buffer- These computers had built-in video which had it's own VRAM. This drasticly improves performance as processor cycles are not stolen away by the video hardware.
Other Pages of Interests
Joaquin Pages
Linux/m68k Links
Hardware Pages